What Is a Laser and How Does It Work for Hair Removal

Laser technology serves as a vital tool in medical aesthetics. It shines for hair removal and skin resurfacing. Now, what is a laser? Deep down, it’s a machine that puts out a tight ray of light. This light has special features—monochromatic, coherent, and collimated. They help it touch exact spots in body tissues. These features let laser treatments hit targets well and work great for beauty uses.
Fundamentals of Laser Technology
Core Components Required for Laser Function
Each laser setup depends on three main parts. They help it work smoothly.
-
A gain medium, which determines the wavelength of the laser beam.
-
An energy source, such as electricity or light, to excite the medium.
-
An optical resonator, typically composed of two mirrors, one fully reflective and the other partially transmissive.
These pieces team up. They create something called stimulated emission. That makes a coherent light ray. The mirrors in the resonator build up this light. They also point it. So, it can focus for healing tasks.
Key Physical Properties of Laser Light
Laser light sets itself apart from everyday light. It does so in some clear ways.
-
Monochromaticity: The light holds just one wavelength. This makes it very picky when touching tissues.
-
Coherence: Every photon stays in step. This allows sharp energy drops.
-
Collimation: The ray spreads very little. It keeps thin over far reaches. That matters a lot for treatments that need focus.
Types of Lasers Used in Medical Aesthetics
A few kinds of lasers see regular use in beauty medicine.
-
Diode lasers (e.g., 808nm) fit best for hair removal on all sorts of skin.
-
Alexandrite lasers (755nm) handle lighter skin and thin hairs nicely.
-
Nd:YAG lasers (1064nm) dive deeper. They keep things safer for dark skin.
Anchorfree’s L300EU laser device utilizes 808nm diode laser technology, combined with 755nm and 1064nm wavelengths, to provide customized treatments for different hair and skin types. You must tweak pulse duration and fluence too. Base it on skin type and goals. This brings good results. And it skips harm.
Mechanism of Laser Hair Removal
Selective Photothermolysis in Hair Follicle Targeting
Laser hair removal builds on selective photothermolysis. Here, certain wavelengths aim for melanin in hair roots.
Diode laser treatment works on the principle of ‘selective photothermolysis,’ an optical technique that points heat at the target hair follicles without damaging the surrounding tissue.
Melanin soaks up the laser energy. It changes light to heat. This hurts the root parts that grow hair. But time counts big. Pulse duration has to match the follicle’s thermal relaxation time. If not, it could hurt close tissues.
Factors Affecting Treatment Efficacy and Safety
A bunch of things shape how treatments turn out.
-
Hair color and skin tone: Darker hair on light skin gives top results.
-
Follicle depth: Deeper roots need longer waves like 1064nm.
-
Cooling systems: Advanced cooling technology enhances patient comfort during sessions by reducing heat buildup.
-
Session frequency: Most patients need 6–10 treatments spaced 4–6 weeks apart for optimal reduction.
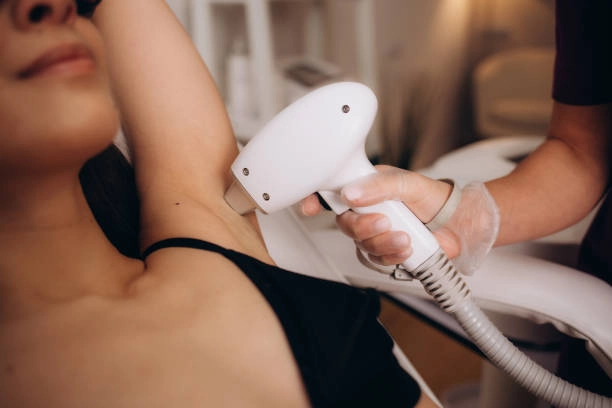

Comparison with Other Hair Removal Techniques
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
Laser hair removal gives clear upsides. It beats shaving and waxing.
-
Results hang on longer—weeks or months over days.
-
Much less ingrown hairs. And less skin itch too.
-
It handles big spots fast. With good aim.
Unlike shaving or waxing, laser hair removal minimizes the risk of ingrown hairs and skin irritation.
Limitations and Considerations for Candidates
Still, laser treatments fall short sometimes.
-
Less effective on light blonde or grey hairs due to low melanin content.
-
Potential side effects include redness, swelling, or rare pigmentation changes.
-
Requires professional evaluation to determine suitability.
Broader Applications in Aesthetic Dermatology
Use of Lasers in Skin Resurfacing Procedures
Lasers also act as strong helpers. They fix skin feel.
Erbium YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet) is an ablative laser, which means it works by removing the outermost layer of the skin to stimulate collagen production and reveal healthier skin beneath.
This way treats:
-
Acne scars
-
Fine lines
-
Uneven tone
-
Sunspots
Erbium YAG hits the sweet spot for patients who want visible results without the more intense healing phase of CO2 lasers. It’s gentler and safer for a broader range of skin tones.
Integration with Other Modalities in Treatment Plans
Lasers mix well with others. Think RF microneedling or chemical peels. Such pairs can:
-
Boost collagen work
-
Fix color spots better
-
Tackle loose skin more surely
This blended path gives full beauty answers. It fits each person’s wants.
Technological Advancements in Laser Devices
Innovations in Pulse Control and Beam Delivery Systems
Fresh laser setups bring:
-
Adjustable pulse durations for safe use across all Fitzpatrick skin types
-
Variable spot sizes that balance precision with speed
-
Multi wavelength configurations to treat mixed hair colors and depths
The combination of the well known 808nm and these other three proven wavelengths will improve penetration depth and safety for darker skin and optimize treatment for different hair colors while obtaining relatively high efficacy of the treatment results.
Anchorfree’s L300EU device exemplifies this innovation with four combined wavelengths (755nm, 808nm, 940nm, 1064nm), adjustable energy up to 50 J/cm², and intuitive software upgrades via USB or SD card.
Safety Enhancements in Modern Laser Platforms
Safety comes first.
The perfect cooling effect makes the operation feel more comfortable.
Anchorfree’s advanced cooling system—featuring compressor and semiconductor technologies—cuts crystal temperatures a good deal versus other devices. It lessens skin top heat. Plus, it ups comfort.
Here’s a quick look at performance metrics:
| Device | Crystal Temp After (°C) | Epidermis Temp After (°C) |
| L300EU | 27.5 | 38 |
| Other Devices | 36.9 | 42.5 |
Such real time thermal control boosts safety. It helps especially for darker skin tones prone to pigmentation issues.
FAQs
Q: What is selective photothermolysis?
It’s a process where specific wavelengths target pigments like melanin without harming surrounding tissue.
Q: How many sessions does laser hair removal require?
Most patients need between 6–10 sessions spaced several weeks apart for long lasting results.
Q: Is diode laser safe for darker skin?
Yes, especially when combined with proper cooling systems and longer wavelengths like 1064nm.
Q: Can lasers remove white or grey hair?
No—lasers target melanin, so they are ineffective on hair lacking pigment.
Q: What makes Anchorfree’s L300EU stand out?
Its four wavelength design and advanced cooling system offer precise, safe treatments across all skin types.